Vacuum Insulation Technologys
With vacuum insulation technology developed in Tiger’s 100-year history, the high insulation performance supports excellent heat and cold insulation packages, energy saving, and ease of use.
We contribute to the development of various industrial fields such as medicine, transport, and space industries.
What is vacuum insulation technology?
Technology that prevents heat from escaping
Vacuum insulation technology removes air from a space to create a vacuum, thereby increasing the thermal insulation effect.
Vacuum insulated bottles are one example of a product that demonstrates this technology.
In a vacuum bottle container, a vacuum is created in the double space, resulting in very high thermal insulation performance.
This keeps the contents warm or chilled for longer periods of time and contributes to energy conservation.
How is heat conducted?
The change in temperature around us is mainly related to the three principles of heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation.
We will explain each of these three phenomena.
01
Conduction
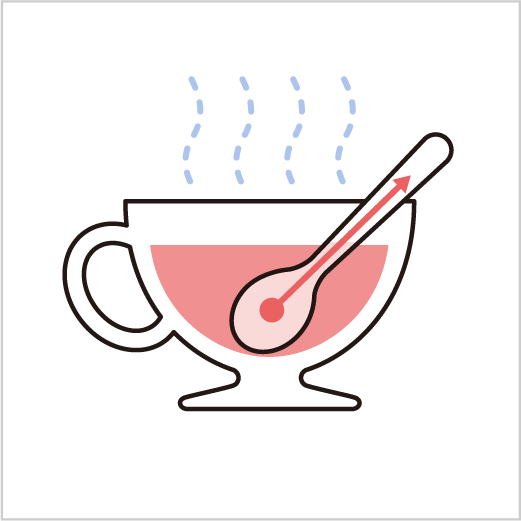

Conduction is defined as a phenomenon of heat transfer through matter. When part of an object is heated, molecular motion in the heated part becomes active.
Collision of these molecules with each other results in the transfer of energy from the high-energy molecules to the low-energy molecules. This process is known as “heat conduction” and the numerical value expressing how well an object conducts heat is termed “heat conductivity”.
For example, when a metal spoon is placed in hot soup, even the spoon handle gets hot because of heat conduction.

02
Convection
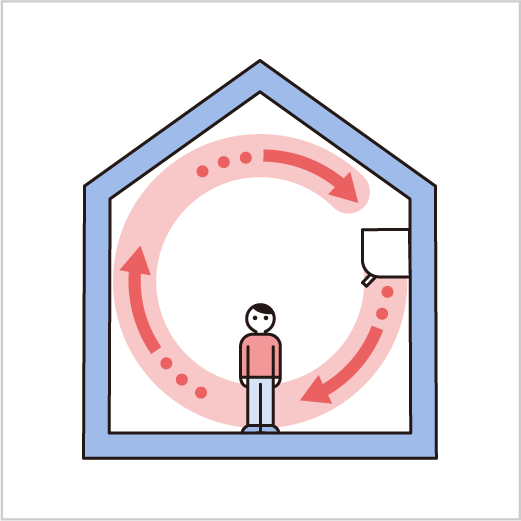
Convection is defined as a phenomenon in which hot air or liquid rises and cold air or liquid falls.
When air is heated, it expands and becomes less dense. The heated air is less dense than the surroundings, and rises by the action of buoyant force. The rising heated air transfers heat to the surroundings by heat conduction.
For example, when a room is heated, warm air rises and cold air sinks. If the air is forced to circulate with a fan in a room, the whole room can be heated efficiently.

03
Radiation
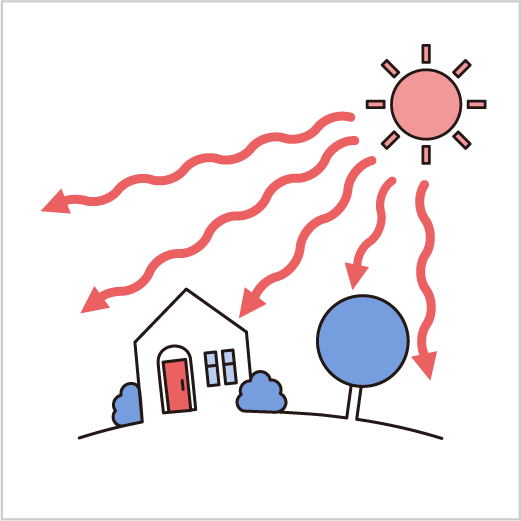
The transfer of heat energy caused by electromagnetic radiation is known as “radiation”, which can be defined as a phenomenon of heat transfer between objects without direct contact.
Despite the absence of direct contact, space is not a vacuum, and the heat of the Sun reaches the Earth via electromagnetic waves such as infrared rays. This process is known as radiation, and it is responsible for the heating of the Earth, as well as various life activities and atmospheric phenomena. The process of radiation involves the transfer of heat energy, with the vacuum of space serving as the medium for this transfer.
For example, the phenomenon of the Earth being warmed by electromagnetic waves such as infrared radiation, as a result of the Sun’s energy, can be considered an example of radiant heat.

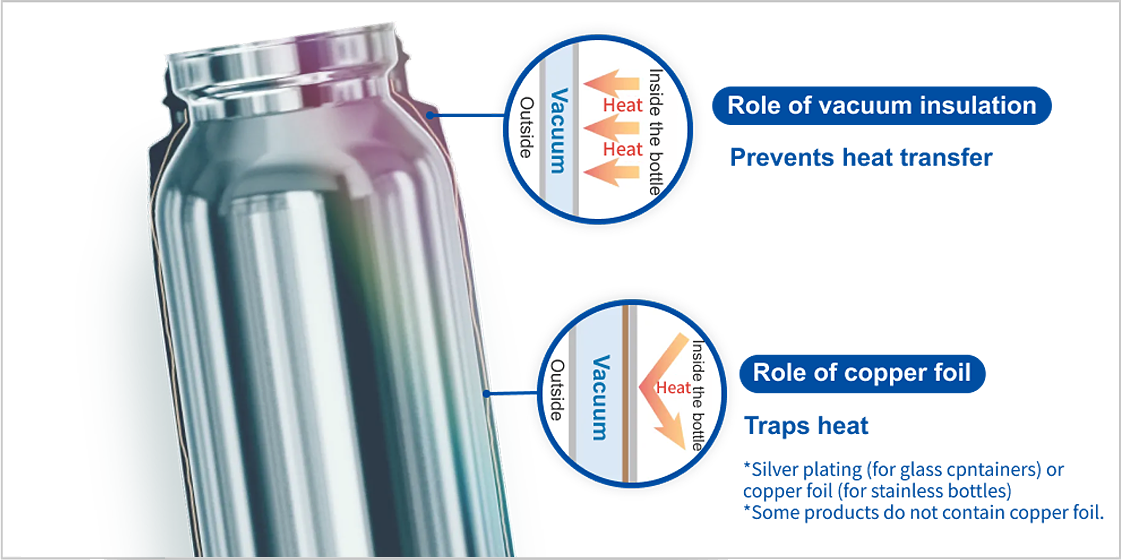
Vacuum insulation
technology
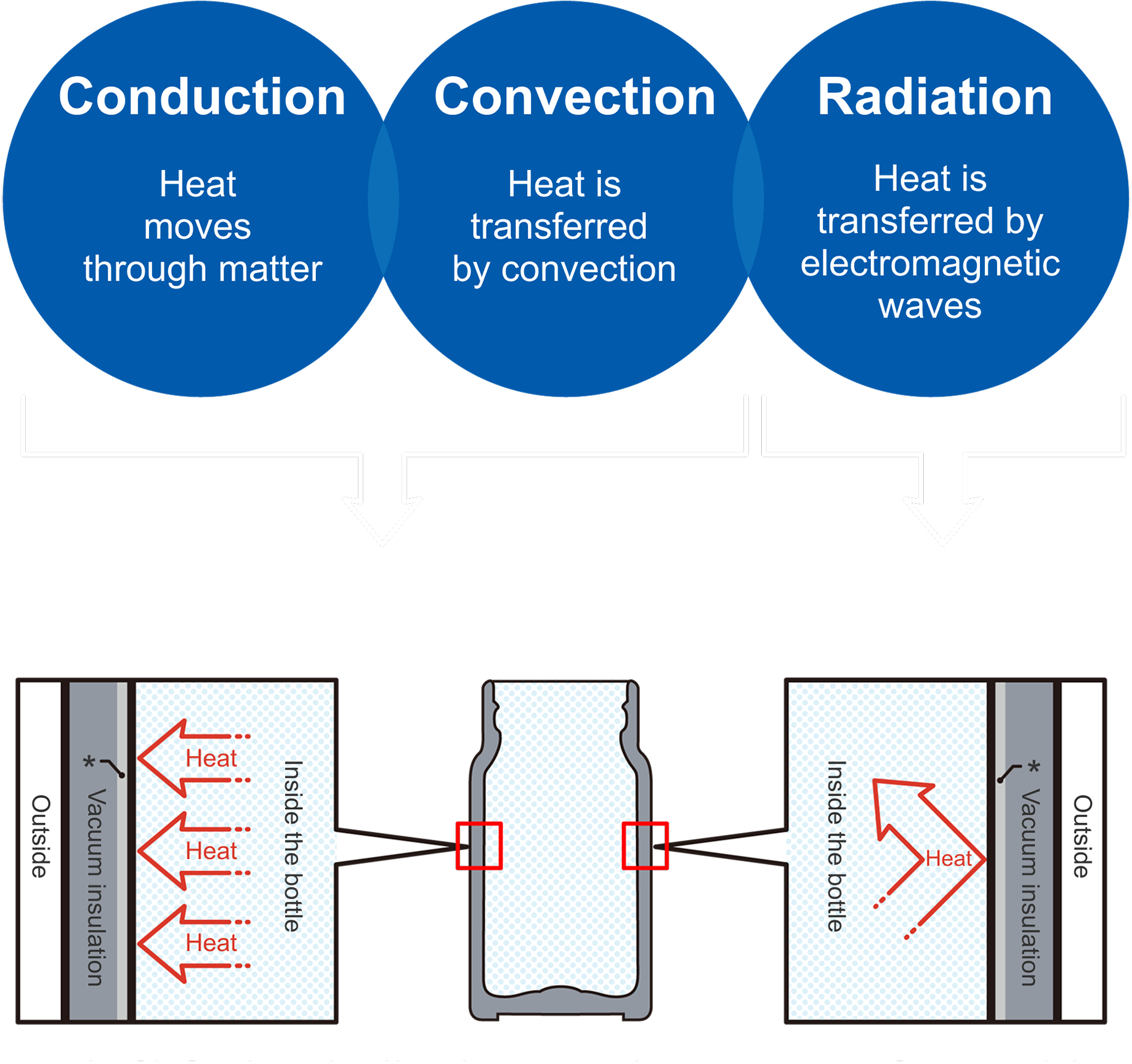
The presence of air and other gases is negligible in a vacuum, thereby effectively suppressing conduction and convection.
Additionally, the mirror finish on the inner surface and the metal foil sandwiched between the vacuum layers reflect radiated heat, thereby preventing temperature changes and providing high heat insulation.
01
Suppression of conduction
In the absence of air molecules, i.e. in a vacuum, heat conduction does not occur.
According to JIS (Japanese Industrial Standards), a vacuum is defined as “a state of a space filled with a gas at pressures lower than atmospheric pressure”, i.e. where there are only a very few air molecules, and thus almost no heat conduction.
02
Suppression of convection
In the absence of air in a given space, neither a warm air layer nor a cold air layer is formed.
It follows that in a vacuum, where there is no air, convection does not take place. The convection phenomenon is caused by buoyant force. Therefore, in a vacuum where no gas exists, no convection takes place.
03
Suppression of radiation
Radiation can transfer heat energy even by means of the vacuum of space as a medium.
In a manner analogous to the manner in which the heat of the Sun reaches the Earth, heat energy is transferred by radiation through a vacuum. For this reason, if the inner surface of a vacuum bottle is mirror-finished or copper foil is placed in the vacuum layer, heat radiation is reflected and heat energy inside the bottle is retained efficiently.
Advantages of vacuum insulation technology
Vacuum insulation technology has the potential to bring about innovation in a variety of fields.
The benefits are not limited to energy saving and environmental contributions.

Energy-saving effect
Vacuum insulation technology provides excellent thermal insulation performance. This increases heat and cold insulation and improves energy efficiency. It significantly reduces energy consumption and contributes to cost reduction.

Contribution to
carbon neutrality
By utilizing vacuum insulation products that do not consume energy, CO2 emissions can be reduced, contributing to carbon neutrality.

Improved accuracy of
temperature control
Because vacuum-insulated products minimize temperature changes, they are also suitable for use in areas where precise temperature control is required. This improves product quality and performance.

Wide range of applications
Vacuum insulation technology has applications in such diverse fields as home appliances, construction, transportation, medicine and space exploration.
Introduction of Vacuum Insulation Technology
Products for Corporate Customers
Here are the corporate products that utilize Tiger’s vacuum insulation technology.

